Climate change is causing the colors of flowers to change due to the increase in uv radiation

Climate Change and its Impact on Flower Colors
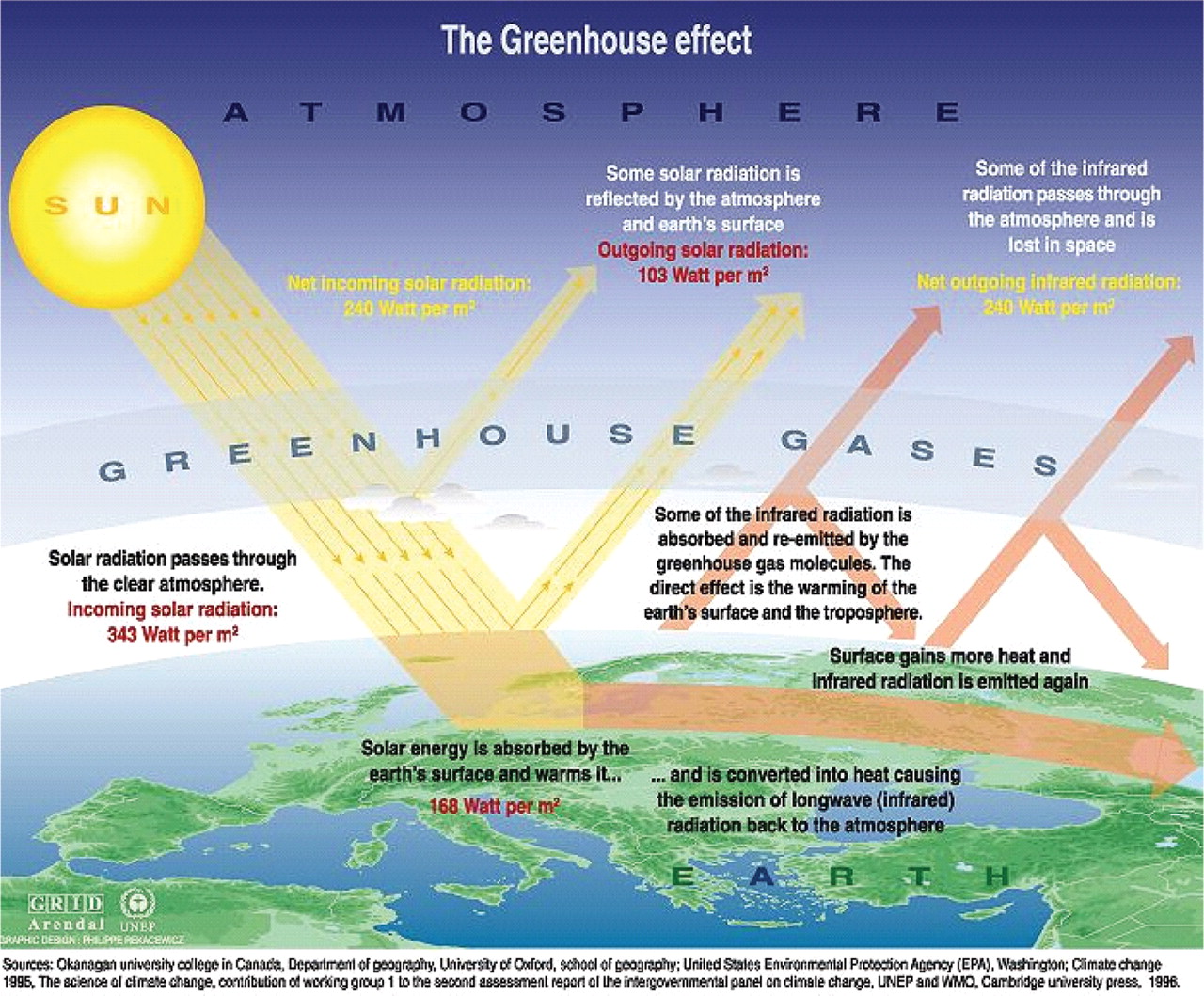
Climate change, a pressing global issue, is altering our planet in various ways. One of the lesser-known effects of climate change is its impact on the colors of flowers. As temperatures rise and the Earth’s climate becomes increasingly unpredictable, scientists have observed a shift in the hues of blossoms worldwide. Recent studies, such as the one reported by News18, suggest that this phenological change is primarily influenced by the increase in ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
The Link Between Climate Change and Flower Colors
Flowers typically utilize pigments, such as anthocyanins and carotenoids, to produce their vibrant colors. These pigments play a crucial role in attracting pollinators and ensuring successful reproduction. However, the rising temperatures caused by climate change result in increased levels of UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. As a defense mechanism against this excessive UV exposure, many plants begin to alter their pigment production.
The increase in UV radiation triggers a series of chemical reactions within the flowers. The plants respond by producing additional protective pigments, leading to changes in coloration. These shifts can be seen in several ways: flowers may appear lighter, darker, or take on different hues altogether. For instance, certain species that once displayed pink blossoms may now showcase more vibrant shades of red, while others may transition towards deeper purple tones.
The Impact on Ecosystems and Biodiversity
The changes in flower colors caused by climate change can have far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and biodiversity. As pollinators are attracted to specific colors, alterations in flower hues may disrupt long-standing relationships between plants and their pollinators. This disruption can negatively impact the reproductive success of both plants and their pollinators, potentially leading to a decline in species populations.
Moreover, these shifts in flower colors can also influence the availability of food sources for various animals. Changes in the timing and structure of floral pigments can affect the feeding habits of herbivores and, consequently, disrupt entire food chains. Consequently, the ecological balance and stability of many ecosystems are at stake.
The Urgency for Conservation Efforts
The observed changes in flower colors as a result of climate change serve as yet another wake-up call for conservation efforts. It emphasizes the need for a collective global response to mitigate the effects of climate change and prevent further ecological disturbances. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adopting sustainable practices, and preserving natural habitats, we can help protect and restore the intricate web of relationships that underpin our planet’s ecosystems.
In conclusion, the effects of climate change extend beyond rising temperatures and extreme weather events. As UV radiation increases due to climate change, flowers are adapting by shifting their colors. This shift in pigmentation not only impacts the beauty of nature but also disrupts vital ecological relationships. By understanding and addressing these changes, we may have a chance to preserve the breathtaking array of flower colors and the biodiversity they support.
Tags
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff


