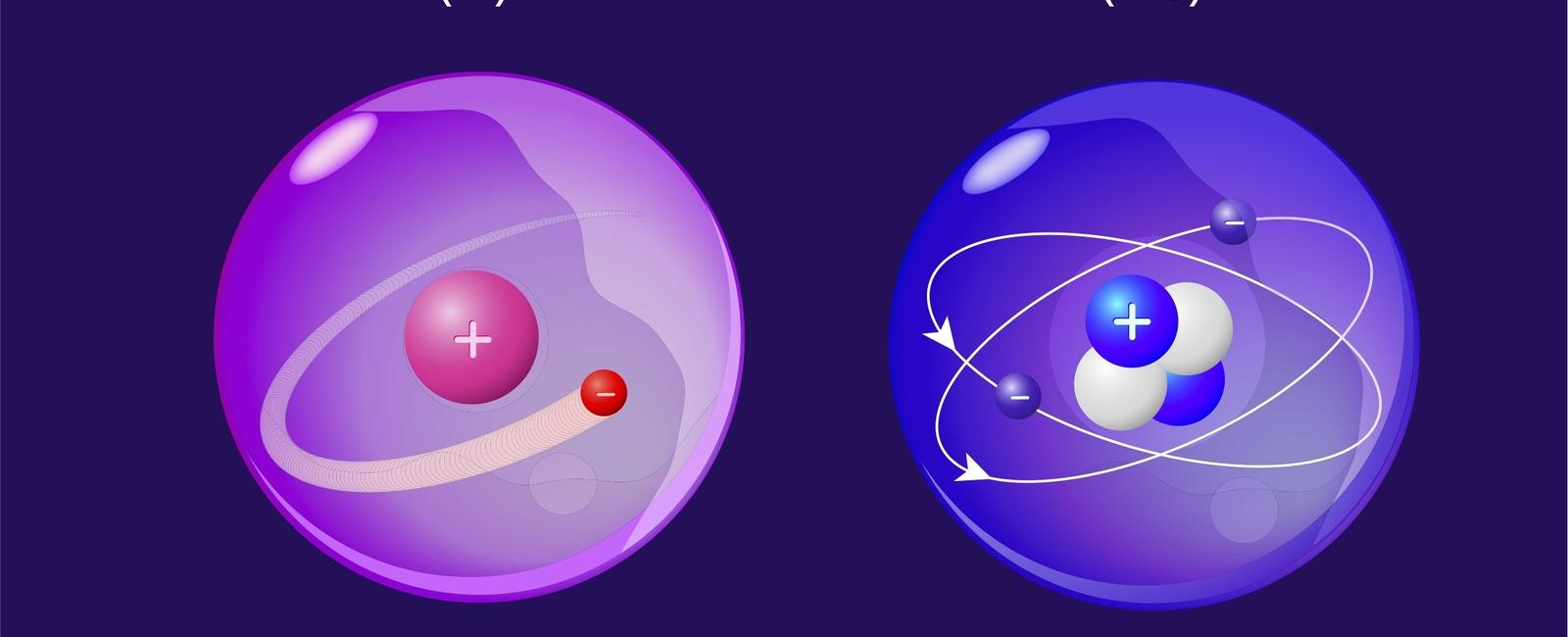
Both helium and hydrogen make up about 99 9 of the ordinary matter in our universe oxygen makes up only a tiny 0 05
The Prevalence of Helium and Hydrogen in the Universe

In our vast and mysterious universe, the composition of ordinary matter is predominantly comprised of two elements - helium and hydrogen. These elements collectively make up an astounding 99.9% of the matter observed in the universe, leaving oxygen with a minuscule share of only 0.05%.
Helium - An Abundant Element in the Cosmos
Helium, a colorless and odorless gas, plays a pivotal role in the constituents of our universe. It is the second most abundant element, comprising approximately 24% of the ordinary matter in the universe. Its presence can be detected in the most remote regions of our cosmos, including deep space and even within stars.

One intriguing fact about helium is that it was first discovered during a solar eclipse in 1868. Its name, derived from the Greek word “helios” meaning sun, directly reflects its connection to our beloved star. The sun is a vast reservoir of helium, with about 70% of its mass consisting of this noble gas.
Apart from being present in stars, helium can also be found in abundance within gas giants, such as Jupiter and Saturn. These planets have an atmosphere rich in helium, with the gas comprising nearly three-quarters of their total composition. Its unique properties make it an essential resource, with applications ranging from cooling superconducting magnets to various medical and industrial uses.
Hydrogen - The Most Common Element
Now let’s talk about the champion of all elements in the universe - hydrogen. This lightest and simplest element takes the crown as the most prevalent substance, accounting for approximately 75% of the universe’s ordinary matter. It is truly the backbone of cosmic chemistry, interacting with other elements to create stars, galaxies, and all the celestial wonders we behold.
The formation of hydrogen dates back to the first moments of the universe’s existence. During the Big Bang, hydrogen gas was produced in abundance and served as the primary building block of the cosmos. This monumental event set the stage for the formation of galaxies and the eventual emergence of life.
Despite its simple atomic structure, hydrogen exhibits remarkable versatility. It fuels nuclear fusion reactions within the cores of stars, releasing vast amounts of energy that illuminate our universe. This process has been ongoing since the birth of the earliest stars, allowing hydrogen to leave its mark on the entirety of the cosmos.
Understanding the prevalence of hydrogen and helium enables us to gain deeper insights into the vastness and complexity of our universe. By investigating and comprehending these key components, we come closer to unraveling the mysteries that lie beyond the boundaries of our small blue planet.
Source: Live Science
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

