Alcohol takes over your body instantly because your stomach sends it directly into your bloodstream it takes only 5 minutes for your brain to react to alcohol then you experience its effects within 10 minutes

Alcohol Takes Over Your Body Instantly: The Impact on Your Brain
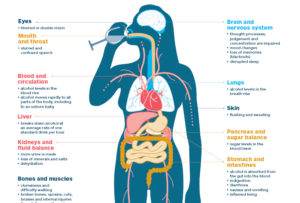
Alcohol, a commonly consumed beverage, has a profound effect on the human body. When you take a sip of alcohol, it swiftly takes over your body, thanks to the direct route established between your stomach and bloodstream. This close connection allows the alcohol to pass through the lining of your stomach walls and enter your bloodstream almost instantly. Once unleashed into your bloodstream, it takes only about five minutes for your brain to react to this powerful substance.

The effects of alcohol on the brain are both fascinating and concerning. This article will delve into some of the intriguing facts behind alcohol’s impact on your brain and body. Let’s explore how alcohol affects the brain and how quickly these effects take hold.
When the alcohol molecules reach your brain, they interfere with the normal communication between neurons, the cells responsible for transmitting information. Alcohol primarily affects the inhibitory neurotransmitter known as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which keeps your brain activity in check. Alcohol enhances the inhibitory effects of GABA, resulting in decreased brain activity and slower response times.
Within just 10 minutes of consuming alcohol, you start experiencing its effects. You may notice a sense of relaxation and reduced inhibitions. As alcohol continues to circulate through your bloodstream, it affects different regions of your brain, leading to various short-term effects. These effects include impaired judgment, diminished coordination, and even changes in mood and behavior.
While moderate alcohol consumption may appear harmless, excessive and prolonged use can lead to severe consequences. Binge drinking, for example, can result in extreme intoxication, potentially causing alcohol poisoning or other life-threatening conditions. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the limits and make responsible choices when it comes to alcohol consumption.
In conclusion, alcohol promptly takes over your body by directly entering your bloodstream once it reaches your stomach. The brain’s response to alcohol occurs within a remarkably short time, approximately five minutes. Within ten minutes, you can experience the initial effects of alcohol, which can alter your judgment, coordination, and behavior. Remember to always prioritize your health and make informed decisions when it comes to alcohol consumption.
Source: Northwestern Medicine
Share
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

