About 50 80 of the earth s oxygen comes from the ocean thanks to oceanic plankton this group includes algae drifting plants and a few bacteria
About 50-80% of the Earth’s Oxygen Comes from the Ocean: The Vital Role of Oceanic Plankton
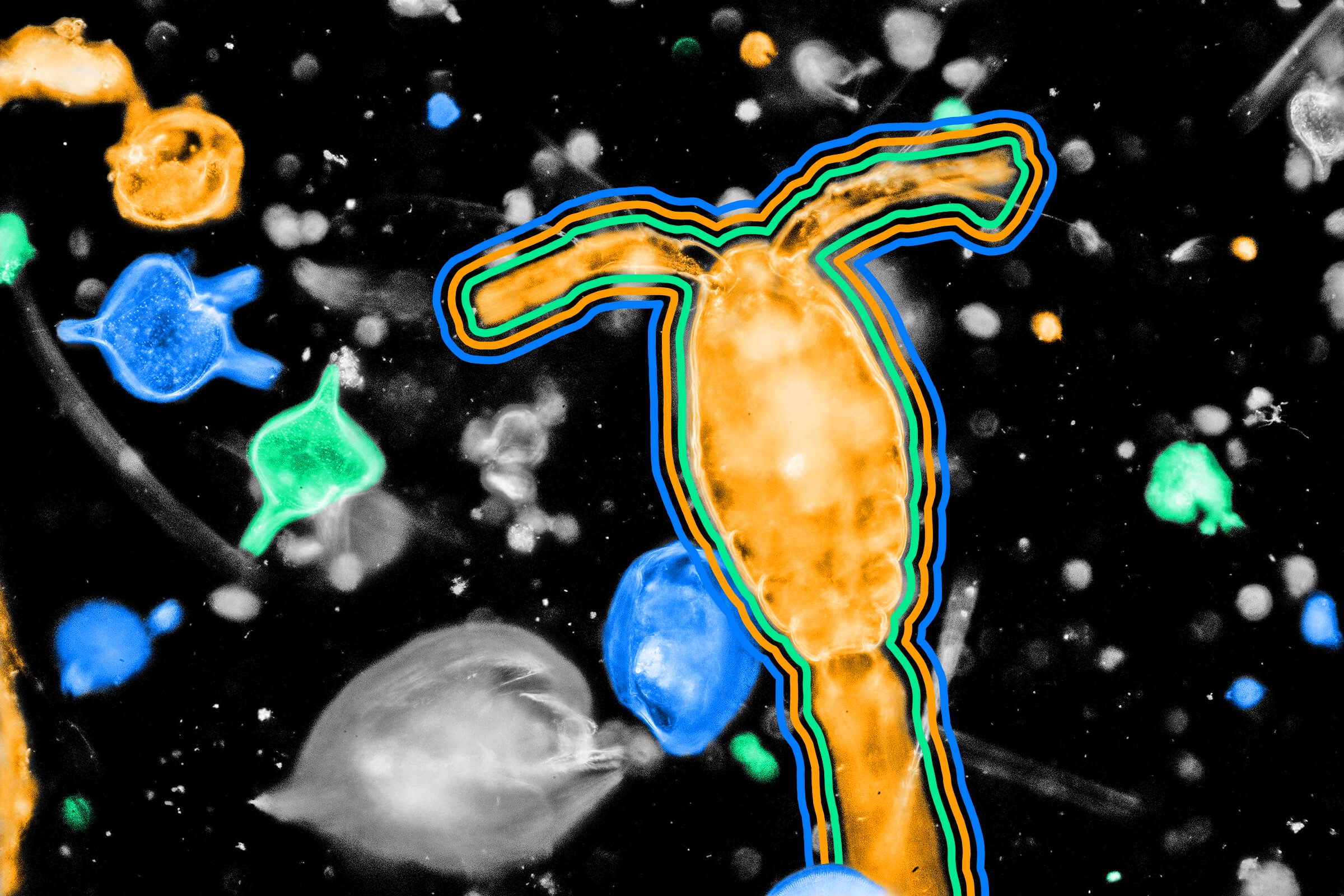

Did you know that the ocean is not only a beautiful and vast body of water but also a significant contributor to the oxygen we breathe? It may come as a surprise, but about 50-80% of the Earth’s oxygen comes from the ocean, thanks to a diverse group of organisms known as oceanic plankton. This group includes algae, drifting plants, and a few bacteria.
Oceanic plankton plays a crucial role in the production of oxygen through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrients into organic compounds and, in the process, release oxygen as a byproduct. These planktonic organisms are responsible for generating a substantial portion of the oxygen we need to survive.
Algae, perhaps the most recognizable member of oceanic plankton, are tiny, plant-like organisms found in both freshwater and marine environments. These microscopic organisms possess chlorophyll, a pigment that allows them to convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. While they may appear insignificant individually, the total biomass of algae in the ocean is enormous, making them a vital part of the global oxygen cycle.

Drifting plants, another type of oceanic plankton, include a wide range of organisms that float freely in the water column. These plants, such as seaweeds and seagrasses, also contribute to oxygen production through photosynthesis. Seaweeds, in particular, are known for their high growth rates and ability to capture large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making them valuable contributors to oxygen production and carbon sequestration.
In addition to algae and drifting plants, certain types of bacteria found in the ocean also play a role in oxygen production. These bacteria, known as cyanobacteria, possess the unique ability to photosynthesize. Cyanobacteria can be found in various marine environments, including surface waters, deep sea sediments, and even polar regions. Though they are less abundant compared to algae and other planktonic organisms, their contribution to oxygen production should not be overlooked.
The significance of oceanic plankton in producing oxygen cannot be emphasized enough. Not only do they provide the majority of the Earth’s oxygen supply, but they also support the overall balance of marine ecosystems. Additionally, these microscopic organisms serve as a critical food source for larger marine animals, forming the basis of the marine food web.
Understanding the vital role of oceanic plankton in oxygen production is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet’s ecosystems. As we continue to face environmental challenges, preserving the health of the ocean becomes crucial for sustaining oxygen levels and mitigating climate change.
Sources:
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

