A dragonfly has a lifespan of 6 months

A Dragonfly Has a Lifespan of 6 Months
Dragonflies are fascinating creatures that captivate our attention with their vibrant colors and graceful flight. They are often seen near freshwater habitats, such as lakes, ponds, and rivers. One commonly known fact about dragonflies is that they have a relatively short lifespan of only 6 months. But why is their life so brief, and what are the factors that contribute to their relatively short existence? Let’s delve into the world of dragonflies to find out more.
Life Stages of a Dragonfly

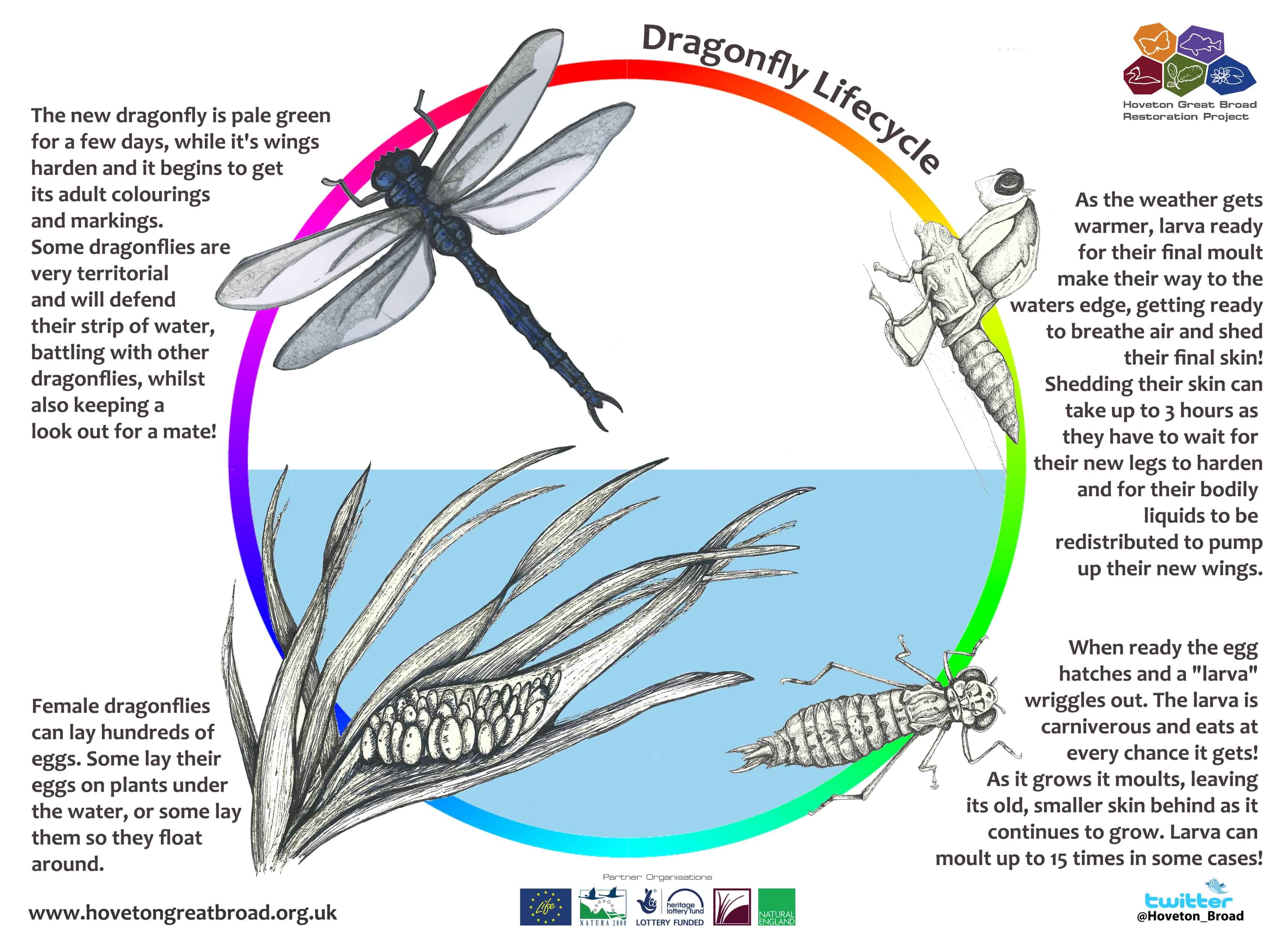
To better understand the lifespan of a dragonfly, it’s crucial to examine their life stages. A dragonfly undergoes a metamorphosis, similar to butterflies but with unique characteristics. Their life cycle consists of four stages:
Egg: The life of a dragonfly begins as an egg. Females typically lay their eggs either in or near water bodies, ensuring the young larvae will have a ready food source upon hatching.
Nymph: Once the eggs hatch, the larvae, known as nymphs, emerge. These juvenile dragonflies spend the majority of their lives in this stage, which can last anywhere from a few months to several years. Nymphs are aquatic and have specialized adaptations for survival underwater.
Emergence: After the nymph stage, the dragonfly enters the pre-adult stage known as emergence. During this phase, the dragonfly leaves the water and climbs onto a plant stem or another surface. The transformation from nymph to adult dragonfly happens inside a hard outer skin known as the exoskeleton.
Adult: Finally, the dragonfly sheds its exoskeleton and emerges as a fully-grown adult. At this stage, the dragonfly’s primary goal is to reproduce. The lifespan of an adult dragonfly is relatively short, usually lasting around 6 months, although some species may live up to a year.
Factors Affecting Lifespan
Several key factors influence the relatively short lifespan of a dragonfly. Let’s explore the main contributing factors:
Predators: Dragonflies are vulnerable to various predators like birds, fish, frogs, and spiders. These natural predators significantly impact the dragonfly population and contribute to their shorter life span. As dragonflies serve as an essential part of the food chain, they are often hunted by larger animals.
Environmental Conditions: The environmental conditions in which dragonflies live can also affect their lifespan. Changes in water quality, temperature, and the availability of food sources can influence their survival rate. These factors pose significant challenges for dragonflies.
Reproduction: Once dragonflies reach adulthood, their primary focus is reproduction. They invest much of their energy in mating and laying eggs, which can take a toll on their overall health and lifespan.
Physical Stress: The physical demands placed on a dragonfly during its brief adult life can also limit its lifespan. The relentless pursuit of prey, territorial disputes, and the energy-intensive process of flight can all contribute to increased wear and tear on their bodies.
It’s important to recognize that despite their relatively short lifespan, dragonflies play a vital role in ecosystems. They help control populations of insects like mosquitoes, gnats, and flies, making them beneficial insects in many ways.
In conclusion, dragonflies have a lifespan of approximately 6 months, although some species might live slightly longer. From their initial stage as eggs, through their development as nymphs, and finally emerging as adult dragonflies, their existence is remarkable and beautiful. The influences of predators, environmental conditions, reproduction, and physical stress are key factors impacting their overall lifespan. Understanding the life cycle and challenges faced by dragonflies deepen our appreciation for these captivating creatures.
Source:
https://www.dragonfly-site.com/how-long-dragonflies-live.html
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

